| .kennel
di Ala D'Oro Bracco Italiano
.Jaap Muller & Tina Steffens |
|||||||||||
|
Hipdysplasia
en Elbowdysplasia
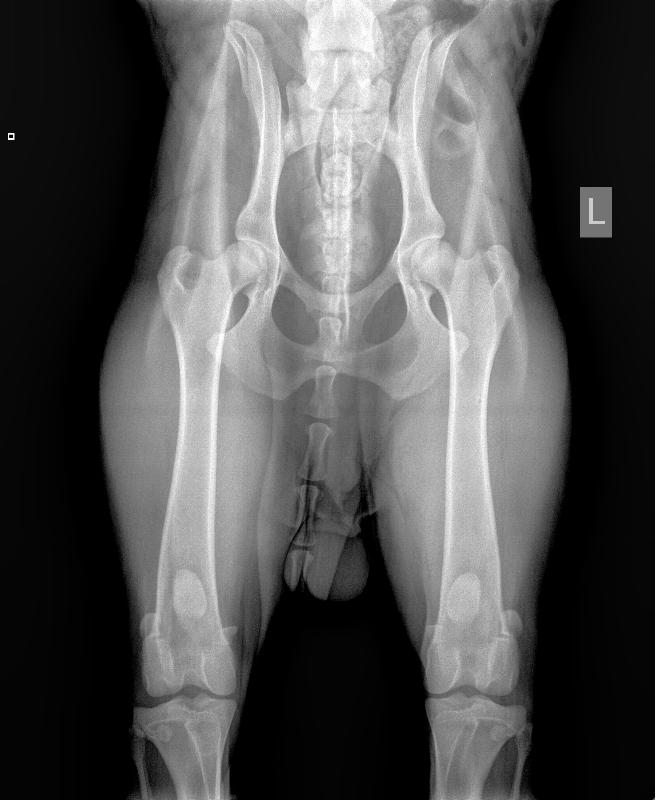
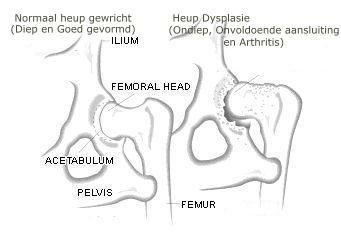
Hip Dysplasia: Is a genetic abnormal development of the hip joints. Some dog have serious nuisance of this abnormality and show bad movement and seem to have pain. Because we know there are different gradation of HD it is possible that we see dogs with HD who don't seem to have any problem. This is why you can not judge the state of HD by looking at the movement of a dog. Reliable information about HD can be given only by x-ray's of the Hip. Click here>>> to read more why x-ray of the hips is important for this breed. At this moment all our dogs have been x-rayed. We think these results are valuable to have so we can say something about the state our bloodlines are in. Individuals with Hipdysplasia results should never be bred with.
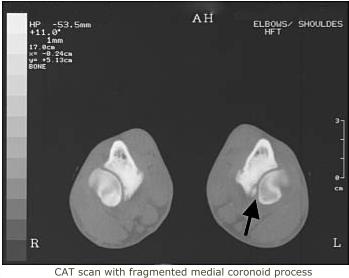
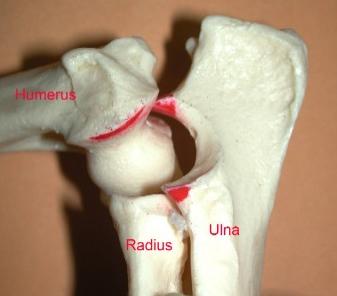
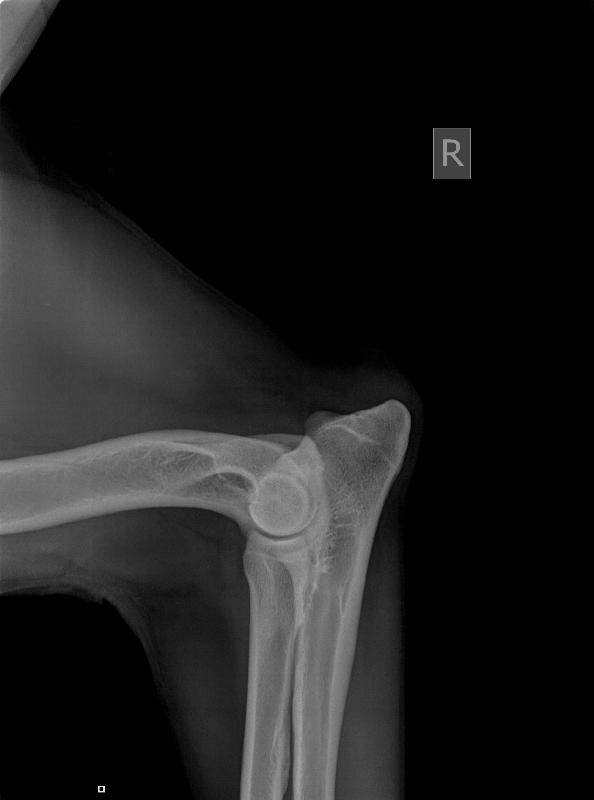
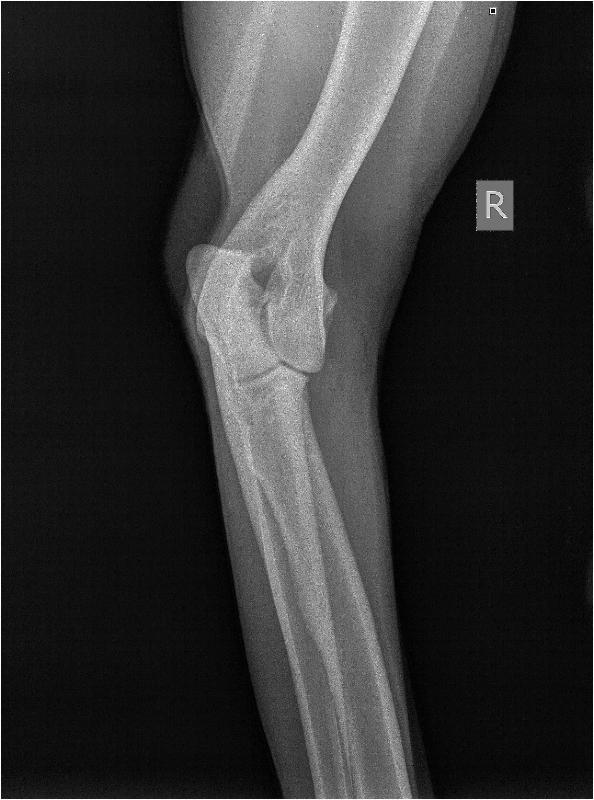
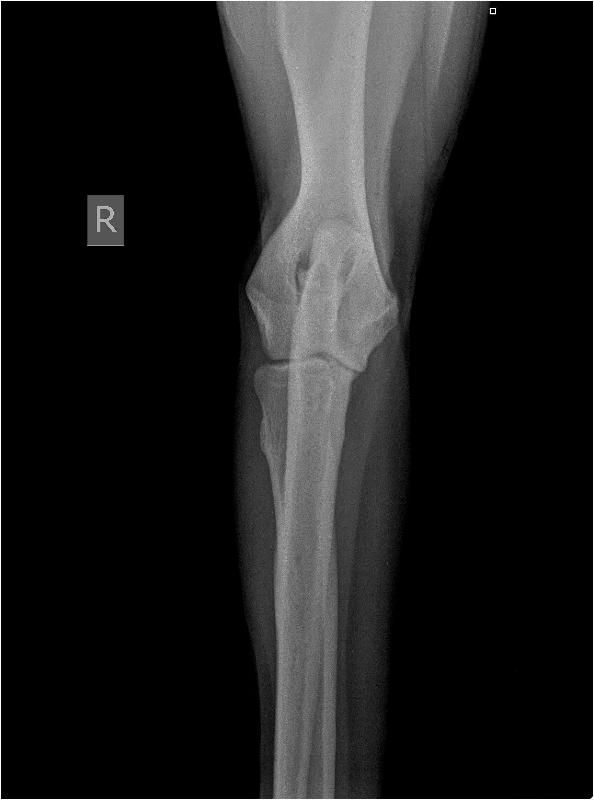
Elbowdysplasia/OCD/LPC:
Elbow Dysplasia is a
developmental degenerative joint disease. This condition is the
result of one or multiple disorder(s) (ununited anconeal process,
fragmented medial coronoid process, or osteochondritis of the medial
humeral condyle). These disorders can either be genetic or environmentally initiated. As is the case with other developmental bone disorders, (such as hip dysplasia) elbow dysplasia is most often found in large dog breeds. Affected dog usually begin to show lameness at about six to seven months of age. Indications of pain can range from mild limping when trotting, altered stance (holds elbow(s) outward from chest), enlargement of the elbow joint, and unable to bear weigh on the affected leg. Rest and pain relievers can occasionally help to lessen the symptoms. X-rays will be necessary for diagnosis and evaluation as to the severity of the condition.
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||